The Ultimate Guide To Geotheta
The Ultimate Guide To Geotheta
Blog Article
Geotheta Can Be Fun For Everyone
Table of ContentsGeotheta Things To Know Before You BuySome Known Incorrect Statements About Geotheta The smart Trick of Geotheta That Nobody is DiscussingSome Known Incorrect Statements About Geotheta 8 Simple Techniques For Geotheta
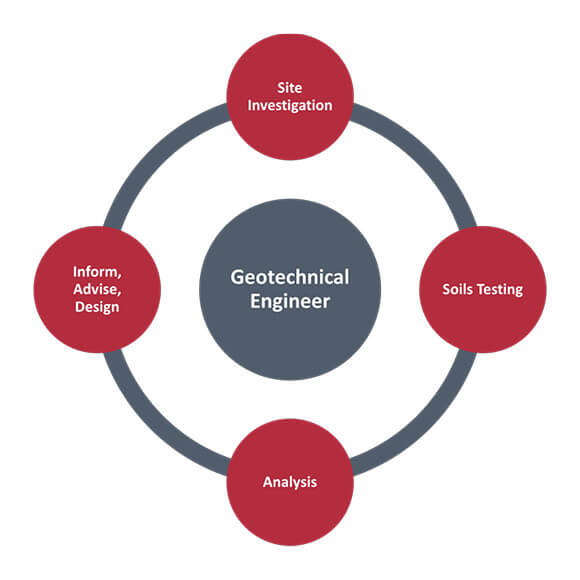
They perform site investigations, gather samples, execute laboratory tests, and evaluate information to review the viability of the ground for building projects - Tailings Engineer. Based upon their findings, geotechnical engineers supply recommendations for structure style, incline security, keeping structures, and mitigation of geotechnical hazards. They team up with various other specialists, such as engineers, architectural designers, and building and construction groups, to make sure that geotechnical considerations are incorporated right into the total project style and implementation
By examining the habits and residential properties of soil and rock, they can recognize possible geotechnical threats such as landslides, soil settlement, or incline instability. Their competence helps prevent failings or mishaps that could threaten lives and residential or commercial property. Below are some comprehensive tasks and responsibilities of a geotechnical engineer: Website Examination: Geotechnical designers conduct site examinations to gather data on subsurface conditions.
They interpret the data to understand the properties and behavior of the dirt and rock, including their stamina, permeability, compaction features, and groundwater problems. Geotechnical Evaluation and Style: Geotechnical engineers analyze the information gathered during site examinations to examine the security and viability of the site for construction projects. They perform geotechnical calculations and modeling to evaluate aspects such as bearing capability, negotiation, slope stability, side planet pressures, and groundwater flow.
Unknown Facts About Geotheta
Foundation Layout: Geotechnical designers play an important role in making structures that can securely support the intended structure. They evaluate the dirt problems and lots requirements to identify the ideal foundation kind, such as superficial foundations (e.g., grounds), deep structures (e.g (https://www.producthunt.com/@geotheta1)., heaps), or specialized methods like dirt enhancement. They consider elements such as settlement limitations, bearing ability, and soil-structure communication to establish optimal structure styles
They evaluate building plans, monitor site activities, and conduct area assessments to validate that the style recommendations are adhered to. If unanticipated geotechnical problems emerge, they evaluate the situation and supply suggestions for remediation or adjustments to the design. Risk Evaluation and Reduction: Geotechnical designers examine geotechnical risks and risks connected with the project site, such as landslides, liquefaction, or soil disintegration.

Cooperation and Interaction: Geotechnical engineers function very closely with various other professionals included in a project, such as architects, structural designers, and construction teams. Reliable interaction and partnership are necessary to integrate geotechnical factors to consider into the total project style and building and construction procedure. Geotechnical engineers supply technological expertise, answer questions, and ensure that geotechnical needs are fulfilled.
8 Simple Techniques For Geotheta
Below are some kinds of geotechnical designers: Foundation Engineer: Foundation designers specialize in creating and examining foundations for structures. They assess the dirt problems, lots needs, and website qualities to identify the most suitable foundation type and style, such as superficial structures, deep foundations, or specialized techniques like heap structures.
They evaluate the factors influencing slope stability, such as dirt buildings, groundwater problems, and slope geometry, and develop methods to prevent incline failures and mitigate threats. Quake Engineer: Earthquake engineers concentrate on assessing and making frameworks to hold up against seismic pressures. They examine the seismic risk of a site, review dirt liquefaction capacity, and create seismic style criteria to guarantee the safety and strength of structures throughout quakes.
They do area testing, collect samples, and analyze the accumulated information to identify the soil properties, geologic formations, and groundwater problems at a site. Geotechnical Instrumentation Designer: Geotechnical instrumentation engineers concentrate on monitoring and measuring the actions of soil, rock, and frameworks. They install and keep instrumentation systems that keep an eye on aspects such as dirt settlement, groundwater levels, incline motions, and structural variations to examine performance and offer very early warnings of potential issues.
The Main Principles Of Geotheta
They perform examinations such as triaxial tests, combination examinations, straight shear tests, and leaks in the structure examinations to collect data for geotechnical analysis and style. Geosynthetics Engineer: Geosynthetics designers specialize in the style and application of geosynthetic materials, such as geotextiles, geogrids, and geomembranes. They utilize these materials to boost dirt security, enhance inclines, supply drain solutions, and control erosion.
They have a tendency to be investigatory people, which you could check here indicates they're intellectual, introspective, and investigative. They are curious, methodical, reasonable, logical, and logical. Some of them are additionally social, suggesting they're kind, charitable, cooperative, person, caring, helpful, understanding, sensible, and pleasant. Does this seem like you? Take our free career test to discover if geotechnical engineer is just one of your leading job suits.
In the office atmosphere, geotechnical engineers utilize specialized software application tools to execute estimations, develop designs, and assess information. They prepare records, review project requirements, connect with customers and staff member, and coordinate task tasks. The workplace setting provides a conducive atmosphere for study, evaluation, and partnership with various other experts associated with the task.
More About Geotheta
They frequently check out project sites to perform website examinations, examine geotechnical conditions, and collect information for analysis. These visits include taking a trip to different areas, in some cases in remote or difficult surfaces. Geotechnical engineers may do dirt tasting, conduct examinations, and screen building activities to make sure that the geotechnical facets of the project are being implemented appropriately.
Geotechnical engineers also function in specialized geotechnical labs. Geotechnical laboratory engineers function thoroughly in these settings, handling testing equipment, running instruments, and recording data.
Report this page